
By having this information available, the raster data structure lists all the cell values in order from the upper left cell along each row to the lower right cell, as illustrated below. This information can be used to find the location of any specific cell. A reference coordinate or x,y location (typically the upper left or the lower left corner of the raster).Geographic properties for a raster typically include This means that each raster dataset typically has a header record holding its geographic properties, and the body of the content is simply an ordered list of cell values. Once the cells or pixels can be accurately georeferenced, it's easy to have an ordered list of all the cell values in a raster. Raster datasets have a special way of defining geographic location. This concept is important to understand: it helps explain how rasters are stored and managed in the geodatabase. These become useful for georeferencing and help explain how raster data files are structured. Rasters in the geodatabase-This strategy is useful when you want to manage rasters, add behavior, and control the schema want to manage a well-defined set of raster datasets as part of your DBMS need to get high performance without loss of content and information (no compression) and want one data architecture for managing all your content.įour geographic properties are typically recorded for all raster datasets.
RASTER FORMAT IN GIS SERIES
This can be a series of independent files, or you can use a technology like ArcGIS Image Server to manage and serve these existing datasets as a collection. Raster provisioning-Getting raster datasets quickly "into play" in your GIS means you will most likely use them as is, typically as a series of raster files.Two data management strategies for rasters are important: The geodatabase provides a very effective means for raster data management in both file and enterprise geodatabases. Users typically employ many raster files, yet many users see an increasing need to manage raster data, along with their other geographic information, in a DBMS. Rasters in the geodatabaseĪ raster is a set of cells arranged in rows and columns and is a commonly used dataset in GIS.

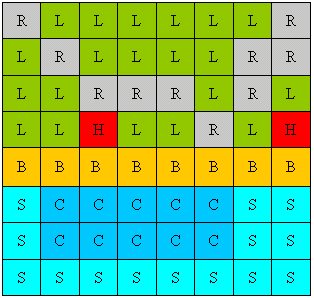
In addition to being a universal data type for holding imagery in GIS, rasters are also heavily used to represent features, enabling all geographic objects to be used in raster-based modeling and analysis. Rasters can be used to represent all geographic information (features, images, and surfaces), and they have a rich set of analytic geoprocessing operators. In the example below, you can see how a series of polygons would be represented as a raster dataset. Often rasters are used as a way to represent point, line, and polygon features.

Raster datasets are commonly used for representing and managing imagery, digital elevation models, and numerous other phenomena. Each cell has a value that is used to represent some characteristic of that location, such as temperature, elevation, or a spectral value. Raster datasets represent geographic features by dividing the world into discrete square or rectangular cells laid out in a grid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
